Hand Surgery
Arthritisc
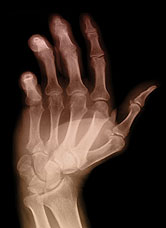
Nearly one in three adults suffers from the swollen, stiff and painful joints of arthritis. Arthritis is the most common chronic ailment among the elderly, although it can affect people of any age, including children.
There are over 100 different types of arthritic diseases. The most common is osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease in which the cartilage protecting the bone ends wears away. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition in which the body’s own immune system attacks the joint lining.
Treatment typically involves a combination of anti-inflammatory medication and devices to relieve stress on the joint (canes, crutches or splints). Regular exercise, weight loss for overweight patients, and cortisone injections may also be helpful. In severe cases, orthopedic surgery such as joint replacement may be the only way to improve or restore function and relieve pain.
Congenital Hand

Congenital deformities of the hand are physical deformities present at birth that can significantly affect a child’s hand function and appearance. Deformities may occur as a result of abnormal development, birth injuries or genetic factors, and can involve fingers that are fused together (syndactyly), an underdeveloped hand (clubhand), extra fingers (polydactyly) and other abnormalities.
Surgical treatment for congenital deformities varies depending on the type and severity of the deformity but may include tendon transfers, skin grafts, limb manipulation, external appliances or prosthetic devices to restore normal function and appearance to the hand. Physical therapy is often needed as well to ensure proper development of hand function in young children.
Wrist pain
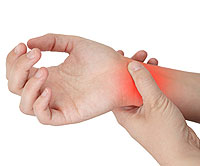
Wrist pain is a common problem with many possible causes. Sometimes it results from a sprain or fracture due to a fall or other injury, while in other cases it may stem from conditions such as arthritis or carpal tunnel syndrome. It is essential, therefore, to obtain the proper diagnosis in order to treat it correctly and effectively.
Wrist arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that can be used to both diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions affecting the wrist joint. During the procedure, your doctor will make several tiny incisions in the wrist, into which a thin tube called an arthroscope and small surgical instruments are inserted. The tube is connected to a camera that displays images of the wrist’s internal structure on a computer screen, allowing your surgeon to precisely identify and target any abnormalities within the joint.
Depending on what is found during the diagnostic procedure, your doctor may choose to treat the condition at the same time. Wrist arthroscopy can be used to remove inflamed areas, repair fractures, remove ganglion cysts and repair torn ligaments or tendons. After surgery, patients should keep the wrist elevated and bandaged for several days in order to reduce the risk of pain and swelling and to promote proper healing.
Fractures/Trauma
Like any other bone in the body, the bones of the hand are susceptible to breaks or fractures, often as a result of excessive force and causing pain, swelling, and limited functioning. There are several different types of fractures which can affect the main body of the bone or just the surface and can include a small crack, a shattering or a complete break through the skin. Fractures of the hand are common because of its many bones and frequent use.
After confirmation of a fracture through X-ray, the affected area is often protected and held in place with a splint or cast. Treatment depends on the type and location of the fracture but often involves surgery to set or repair the bone. Wires, pins, plates or screws, which may or may not be removed at a later date, may be needed to hold the bone in place.
Trigger finger

Trigger finger is a condition that involves one of the fingers becoming stuck in a bent position and then rapidly straightened like the trigger of a gun. This condition is caused by a narrowing of the sheath that surrounds the tendons in the finger, and is common in people who perform repetitive gripping actions. It is also more common in women and people with diabetes. Trigger finger causes stiffness, pain and may eventually lead to an inability to completely straighten the finger.
Mild cases of trigger finger can often be treated through conservative home methods such as rest, finger exercises and avoiding repetitive movements. More severe cases may need anti-inflammatory medication, steroids or surgery. Dr. Galaria will help you decide which treatment is best for you depending on your individual case.
Ganglions Cysts
Ganglions are fluid-filled cysts commonly found on the tendons and joints of the wrists or hands. They may develop suddenly or over time and appear as a small, raised lump near your wrist or finger joints. While ganglions are usually benign and harmless, cysts may put pressure on nearby nerves, potentially causing pain, weakness or numbness.
The specific cause of ganglions is unknown, although they tend to occur in patients with osteoarthritis, and are most common in women between the ages of 25 and 45. They often occur spontaneously when the soft sheath around a tendon or joint swells and fills with mucus.
Despite the lack of complications associated with ganglion cysts, you should still seek medical attention if you notice a lump on your wrist or hand. Treatment is not always necessary, but many wish to have the cyst removed for cosmetic reasons or to relieve pain that has developed over time. Ganglions can be treated through a variety of methods, depending on the size and severity of the cyst. Some of these treatments include:
Immobilization – Resting the wrist or wearing a splint can often release pressure on the nerves to relieve pain, and also decrease the size of the cyst.
Aspiration – This minimally invasive procedure involves draining the fluid from the cyst with a syringe.
Surgery – Surgery may be recommended for cysts that are very painful or interfere with joint movement.
Carpal Tunnel

Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition involving numbness, pain, tingling and instability in the wrist, hand and fingers. It occurs when pressure is put on a nerve in the wrist called the median nerve, which controls motor function in the wrist and hand. This pressure, called impingement, is most often caused by bone spurs, rheumatoid arthritis, repetitive use or injury.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can be diagnosed with tests such as an electromyogram or a nerve conduction study. It can often be effectively treated with nonsurgical therapies such as wrist splints, anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids. In cases where pain and numbness persist, surgery (usually endoscopic surgery) may be necessary to relieve pressure on the nerve.
 703-327-3173
703-327-3173

